Discover how workflow automation is reshaping the U.S. workplace in 2025, empowering professionals to boost productivity, reduce repetitive tasks, and stay competitive. Learn practical strategies, tools, and insights to implement automation in your daily work.
In 2025, one of the most disruptive and compelling shifts in the U.S. workplace is the rise of workflow automation. From small teams in startups to massive enterprises, the push to automate repetitive tasks, streamline operations, and free human talent for higher-value work has never been stronger. According to trend-tracking data, “workflow automation” is among the exploding search topics in the United States. Exploding Topics+2Ahrefs+2
For U.S. professionals, knowledge workers, and business owners, understanding automation isn’t optional—it’s imperative for remaining competitive, efficient, and adaptive in an era of rapid technological change.
workflow automation 2025, future of work, automation tools, workplace productivity, digital transformation, AI automation, low-code tools, workflow automation U.S.
In this article we’ll explore:
- What workflow automation is and why it matters in 2025
- Key driving forces behind its rise in the U.S. market
- How automation is impacting job roles, productivity and company culture
- Practical steps U.S. professionals can take to adopt automation
- Risks, challenges and ethical considerations
- Future outlook: what’s next for workflow automation
By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to harness this trend for your role, whether you’re a freelancer, team lead, or full-time employee.
1. What Is Workflow Automation?
Workflow automation refers to the use of software tools, AI, robotic process automation (RPA), and other digital technologies to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that historically required manual effort. These tasks might include data entry, report generation, email routing, approval workflows, scheduling, alerts, and more.
Automation allows organisations and individuals to reduce human error, speed up processing time, increase consistency, and free up human capital for more strategic and creative activities. As one consultancy put it, automation is being “woven into the fabric of our lives”. Deloitte
In practice, workflow automation might involve:
- A tool that automatically routes invoices for approval, sends reminders, and flags exceptions.
- A system that pulls data from a CRM, compiles a dashboard, and emails insights to the leadership team.
- A marketing stack where a lead triggers a sequence of actions, messages, and tasks without human intervention.
- A team using low-code automation platforms to build internal workflows (e.g., automatic backups, alerts, scheduling).
From a U.S. professional perspective, this trend is less about robots taking over jobs and more about augmenting humans, letting people focus on judgment, strategy, relationship-building, and innovation.
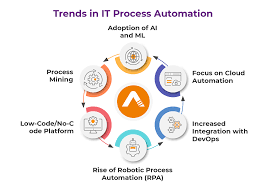
2. Why It Matters Now (Especially in the U.S.)
Several converging factors explain why workflow automation is accelerating and gaining urgency in 2025 in the U.S. context:
2.1 Talent Shortages & Rising Costs
Many U.S. industries face talent shortages, wage inflation, and retention challenges. Automation helps mitigate the pinch by making teams more efficient, reducing dependency on plentiful staff for mundane tasks.
2.2 Shrinking Attention Spans & Demand for Speed
Customers, internal stakeholders, and markets expect faster turnaround, real-time insights, and agile responses. Automated workflows accelerate time-to-action and improve responsiveness.
2.3 Proliferation of No-Code/Low-Code Tools
What once required heavy IT investment is now accessible via no-code/low-code platforms. U.S. professionals, even outside IT, are empowered to build automations themselves, enabling “citizen automation”.
2.4 Rise of Hybrid & Remote Work
The shift to hybrid/remote work means fewer manual hand-offs, fewer in-person coordination opportunities, and a greater need for reliable digital workflows. Automation fills the gap. For example, a recent analysis of U.S. social media strategy noted short-form content and automation of marketing workflows as core to 2025. Sendible
2.5 Strategic Advantage & Competitive Pressure
In a highly competitive U.S. business environment, organisations that adopt automation gain cost, speed, error-reduction, and scale advantages over peers. The pressure to keep up is real.
2.6 Regulatory & Compliance Complexity
With growing regulatory burdens in data, privacy, labour, and financial domains, automation provides controls, audit trails, and governance — making compliance more manageable and consistent.
3. Impacts on the U.S. Workforce and Organizational Culture
Automation is not just a technology change; it has wide-ranging implications for people, roles, culture, and the structure of work.
3.1 Shifting Job Roles and Skills
As automation handles more routine tasks, human roles evolve toward:
- Strategic thinking, problem-solving and decisioning
- Creative collaboration, innovation, and human-to-human interaction
- Data interpretation, exceptions handling, and automation-oversight
For U.S. professionals, this means developing skills like: automation design, process thinking, data literacy, change management, and adaptability.
3.2 Productivity Gains, But Not Without Adjustment
Studies show organisations implementing automation gain productivity, but they also face transitional challenges: employees need training, workflows must be redesigned, change management is essential. Without proper planning, automation can create confusion, shadow processes, or disengagement.
3.3 Culture of Continuous Improvement
Automation fosters a mindset of continuous improvement: map the process → identify repetitive tasks → apply automation → monitor outcomes → refine. U.S. companies seeking innovation now embed this loop into their culture.
3.4 Work-Life Balance and Employee Experience
By removing tedious tasks, automation can reduce burnout and free knowledge workers for more rewarding work. This is especially relevant in the U.S., where employee well-being is increasingly linked to retention, productivity, and employer brand.
3.5 The Risk of Automation-Backlash
However, there are risks: if automation is implemented without transparency, without employee involvement, or leads to job elimination fears, it can damage morale and trust. For U.S. firms—especially those with unionised workforce or high employee expectations—change management is non-optional.
4. Practical Strategies for U.S. Professionals to Adopt Workflow Automation
If you’re working in the U.S.—whether as a freelancer, team lead, or individual contributor—here are actionable steps to harness workflow automation effectively:
4.1 Understand and Map Your Current Workflows
Start by documenting recurring tasks in your role or team. Use process-mapping tools or even simple spreadsheets to identify:
- Which tasks are repetitive and rule-based
- Which tasks involve manual hand-offs
- What data moves between systems or people
- Bottlenecks, delays, error points
4.2 Prioritise High-Impact Automations
Not every task should be automated. Use a scoring approach: tasks that are frequent, time-consuming, error-prone, and depend on manual effort are best candidates. Focus first on quick-win automation projects.
4.3 Choose the Right Tools
In the U.S., there is a rich ecosystem of automation platforms: low-code/no-code (like Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, Make), RPA tools (UiPath, Automation Anywhere), workflow platforms (Monday.com, Asana), and AI-enabled workflow modules. Consider: cost, learning curve, integration with your existing stack, and support.
4.4 Build Small, Iterate Quickly
Adopt an agile mindset: automate a small piece of the workflow, measure results, refine, then expand. This reduces risk, builds trust, and demonstrates value early.
4.5 Engage Your Team and Stakeholders
Successful automation in U.S. workplaces requires buy-in. Communicate clearly why you are automating, what tasks will be affected, how it will benefit the team, and what the expected outcomes are. Provide training and designate automation champions.
4.6 Monitor, Measure & Adjust
Set KPIs–for example: time saved, error reduction rate, volume of manual hand-offs eliminated, cost savings. Use dashboards to track results. Continuously gather feedback from users and refine workflows.
4.7 Focus on Ethical & Transparent Automation
U.S. professionals must consider: data privacy, auditability, fairness of automated decisions, impact on employees. Make sure to document logic, maintain oversight, and keep humans in loop especially for critical decisions.
4.8 Scale Up Thoughtfully
Once pilot automations succeed, scale them across functions. But beware of spreading too fast without governance—shadow automations can create risk. Set standards for automation creation, monitoring, and maintenance.
4.9 Keep Learning & Stay Adaptive
Automation tools evolve quickly. Stay current with developments (AI-embedded workflow modules, intelligent automation, hyper-automation). In the U.S., continuous learning is a differentiator.
5. Risks, Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Automation brings big promise—but also real risks and management challenges.
5.1 Hidden Complexity
What starts as “automate this simple task” may reveal complex edge-cases, dependencies, or unexpected exceptions. Without proper process mapping and error handling, automation may break down.
5.2 Over-Automation or Poor Design
Automating the wrong tasks or creating brittle systems can lead to failure or frustration. Humans should still supervise, and systems must be robust, flexible, and maintainable.
5.3 Job Displacement & Employee Morale
While automation often augments human work, some roles may change or disappear. U.S. companies must be sensitive: change communications, reskilling programs, transparency about future roles are vital.
5.4 Data Privacy, Compliance & Security
Automated workflows often move sensitive data across systems. U.S. professionals must ensure compliance with regulations (e.g., data protection, industry-specific compliance), secure integrations, and maintain access controls.
5.5 Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
If automation involves decision-making (e.g., loan approval, recruitment, routing), you must assess bias, ensure transparency, and maintain human oversight—especially relevant for U.S. regulatory and ethical environments.
5.6 Maintenance, Governance & Ownership
Automations require maintenance, monitoring and governance. In many U.S. firms, lack of clear ownership leads to broken workflows, outdated automations, or “zombie bots”.
5.7 Cost and ROI Uncertainty
Initial investment (tool cost, training, change management) may not pay off immediately. U.S. professionals must plan realistic timelines, ensure alignment with business goals, and manage expectations.
6. Future Outlook: What’s Next for Workflow Automation
Looking toward the remainder of 2025 and beyond, several key trends will accelerate in the U.S. automation space:
6.1 Hyper-Automation & AI Integration
Automation will move beyond simple rule-based tasks to smart, AI-driven workflows: natural language processing, computer vision, predictive analytics. The line between human and machine workflow will continue to blur. Deloitte+1
6.2 “Automation First” Culture
Organizations will embed automation thinking into every process design from day one (“automate by default”), rather than retrofitting it.
6.3 Citizen Developers & Democratization
In the U.S., non-IT professionals will increasingly build automations using low-code tools. Governance frameworks will shift accordingly.
6.4 Focus on Workflow Resilience
As disruptions (remote work, hybrid models, macro-economic shifts) continue, U.S. organizations will invest in resilient digital workflows that can scale, adapt, and pivot quickly. S&P Global
6.5 Ethical, Transparent Automation Standards
Regulators and stakeholders will demand more transparency, oversight and ethics in automated decision-making. The U.S. regulatory environment will evolve. hottopics.ht
6.6 Integration of Workflows Across Silos
The future lies in end-to-end workflow automation: cross-departmental, integrated systems rather than isolated bots. For U.S. professionals, that means focusing on broader process transformation, not just task automation.
7. Case Study Snapshot
Consider a mid-sized U.S. marketing team: they were spending 20 hours/week on manual reporting, lead-routing, campaign scheduling, and approval workflows. They implemented a low-code automation platform, built workflows that: route leads, update CRM, trigger emails, generate dashboards, and alert relevant stakeholders.
Result:
- Reporting time dropped by 60%
- Lead response time improved by 30%
- The team refocused on creative strategy and audience insights
- Employee satisfaction improved (fewer repetitive tasks)
- ROI achieved within 9 months
This is illustrative of what many U.S. teams are experiencing—and what you can replicate.
8. How This Impacts You (Professionally)
If you’re a U.S. professional, here’s how to think about personal impact:
- As an individual contributor: Learn automation tools, start small in your role, become the go-to person for workflow improvement.
- As a team lead: Map your team’s workflows, prioritise high-impact automations, measure outcomes, celebrate wins, manage change.
- As a freelancer or solopreneur: Automate client onboarding, scheduling, invoicing, report generation—free up your time for growth and strategy.
- As a business owner/executive: Set an automation vision, build governance, invest in skills, integrate across teams, and monitor ROI.
By aligning your skills and mindset with the automation wave, you’ll position yourself for success in 2025 and beyond.
9. Quick Checklist: 10 Steps to Get Started
- Identify 3-5 repetitive tasks in your role.
- Map the process → inputs → outputs → hand-offs.
- Choose one quick-win task for automation (frequent + high time cost).
- Select a tool aligned with your budget and stack.
- Build a prototype workflow with a clear owner and timeline.
- Test with real users, gather feedback, refine.
- Define and track KPIs (time saved, errors reduced).
- Communicate with stakeholders about the change and benefits.
- Document the automation: logic, ownership, exception-handling.
- Review quarterly: retire old workflows, scale successful ones, embed automation culture.
10. Conclusion
As we move through 2025, workflow automation is not just a buzzword—it is a fundamental shift in how American professionals work, compete, and add value. The opportunity is immense: reduce repetitive tasks, improve accuracy, accelerate decision-making, free talent for strategic work, and build resilient, adaptable organisations. But seizing that opportunity demands awareness, action, and foresight.
If you act now—by mapping your workflows, prioritising automations, selecting the right tools, engaging your team, and measuring outcomes—you’ll not only stay ahead of the curve but become a leader in your field. Automation isn’t coming tomorrow—it’s here now. Embrace it, shape it, and let it empower you.
Internal Linking Suggestions:
- Link to posts about “No-Code/Low-Code Tools for Professionals”
- Link to “Future Skills for U.S. Workforce 2025”
- Link to “Hybrid Work & Digital Transformation in U.S. Companies”
External Linking Suggestions:
- Reference big-consultancy reports on automation and tech trends.
- Link to vendor websites for automation platforms (for tool selection).
- Link to research on productivity gains via automation.